import cv2
import numpy as np
from google.colab.patches import cv2_imshow
from tqdm import tqdm
protoFile_body_25b = "pose_deploy.prototxt"
weightsFile_body_25b = "pose_iter_XXXXXX.caffemodel"
BODY_PARTS_BODY_25B = {0: "Nose", 1: "LEye", 2: "REye", 3: "LEar", 4: "REar", 5: "LShoulder", 6: "RSoulder",
7: "LElbow", 8: "RElbow", 9: "LWrist", 10: "RWrist", 11: "LHip", 12: "RHip", 13: "LKnee",
14: "RKnee", 15: "LAnkle", 16: "RAnkle", 17: "Neck", 18: "Head", 19: "LBigToe",
20: "LSmallToe", 21: "LHeel", 22: "RBigToe", 23: "RSmallToe", 24: "RHeel"}
POSE_PAIRS_BODY_25B = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 17], [0, 18], [1, 3], [2, 4], [5, 7], [5, 17],
[6, 8], [6, 17], [7, 9], [8, 10], [11, 13], [11, 17], [12, 14], [12, 17],
[13, 15], [14, 16], [15, 21], [16, 24], [19, 20], [20, 21], [22, 23], [23, 24]]
classes_coco = ["person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle",
"airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light", "fire hydrant",
"stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse",
"sheep", "cow", "elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack",
"umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee", "skis",
"snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard",
"surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife",
"spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog",
"pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch", "potted plant", "bed", "dining table",
"toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard",
"cell phone", "microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator",
"book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier", "toothbrush"]
classes_custom = ["sit", "stand", "lieDown"]
print(cv2.__version__)
print(cv2.cuda.getCudaEnabledDeviceCount())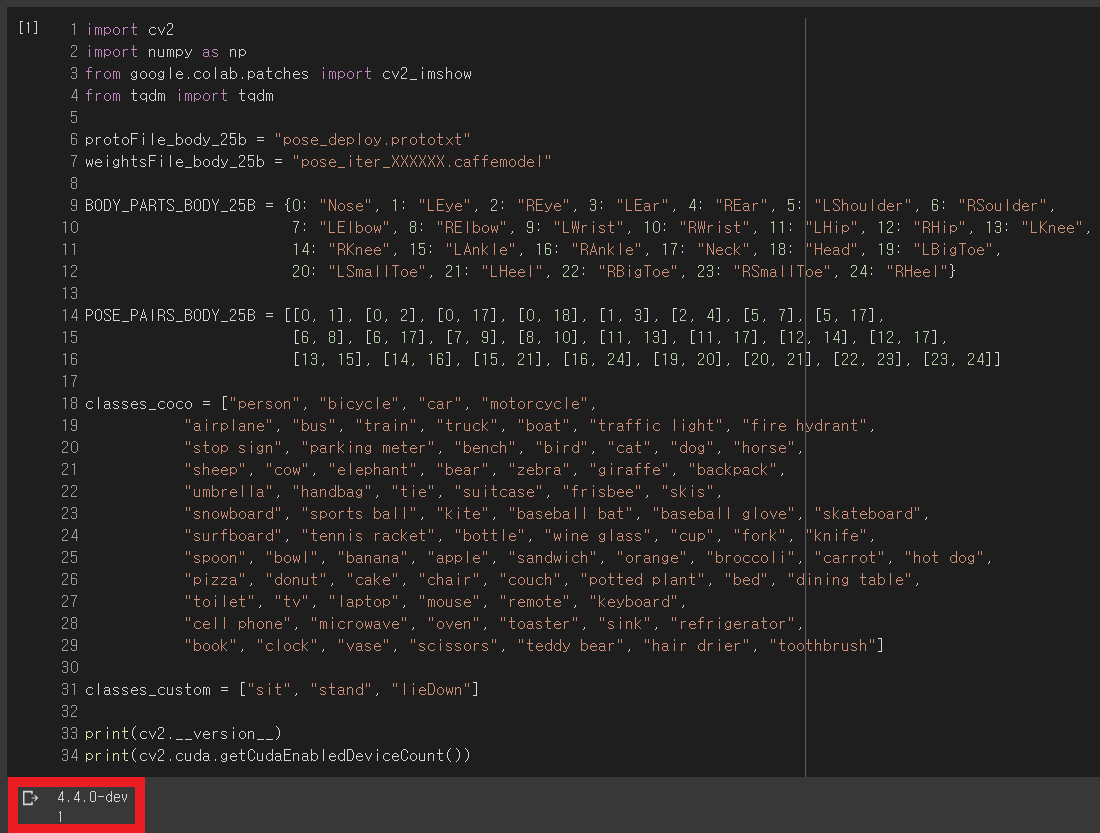
def output_keypoints(threshold, BODY_PARTS):
global points
# 네트워크 지정
net = net_openpose
# 입력 이미지의 사이즈 정의
image_height = 368
image_width = 368
# 네트워크에 넣기 위한 전처리
input_blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1.0 / 255, (image_width, image_height), (0, 0, 0),
swapRB=False, crop=False)
# 전처리된 blob 네트워크에 입력
net.setInput(input_blob)
# 결과 받아오기
out = net.forward()
# The output is a 4D matrix :
# The first dimension being the image ID ( in case you pass more than one image to the network ).
# The second dimension indicates the index of a keypoint.
# The model produces Confidence Maps and Part Affinity maps which are all concatenated.
# For COCO model it consists of 57 parts – 18 keypoint confidence Maps + 1 background + 19*2 Part Affinity Maps. Similarly, for MPI, it produces 44 points.
# We will be using only the first few points which correspond to Keypoints.
# The third dimension is the height of the output map.
out_height = out.shape[2]
# The fourth dimension is the width of the output map.
out_width = out.shape[3]
# 원본 이미지의 높이, 너비를 받아오기
frame_height, frame_width = frame.shape[:2]
# 포인트 리스트 초기화
points = []
for i in range(len(BODY_PARTS)):
# 신체 부위의 confidence map
prob_map = out[0, i, :, :]
# 최소값, 최대값, 최소값 위치, 최대값 위치
min_val, prob, min_loc, point = cv2.minMaxLoc(prob_map)
# 원본 이미지에 맞게 포인트 위치 조정
x = (frame_width * point[0]) / out_width
x = int(x)
y = (frame_height * point[1]) / out_height
y = int(y)
if prob > threshold: # [pointed]
cv2.circle(frame_openpose, (x, y), 5, (0, 255, 255), thickness=-1, lineType=cv2.FILLED)
cv2.circle(frame_zeros, (x, y), 5, (0, 255, 255), thickness=-1, lineType=cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(frame_openpose, str(i), (x, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 1,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
points.append((x, y))
else: # [not pointed]
cv2.circle(frame_openpose, (x, y), 5, (0, 255, 255), thickness=-1, lineType=cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(frame_openpose, str(i), (x, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 0, 0), 1,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
points.append(None)
return frame_openposedef output_keypoints_with_lines(POSE_PAIRS):
# POSE_PAIRS 갯수만큼 RGB 배열을 생성 (frame_zeros에 쓰일 색)
colors = []
for i in range(3):
value_r = value_g = value_b = 50
for j in range(int(len(POSE_PAIRS_BODY_25B) / 3)):
if i == 0:
value_b += 31
if i == 1:
value_g += 31
if i == 2:
value_r += 31
colors.append((value_b, value_g, value_r))
for index, pair in enumerate(POSE_PAIRS):
part_a = pair[0] # 0 (Head)
part_b = pair[1] # 1 (Neck)
if points[part_a] and points[part_b]:
cv2.line(frame_openpose, points[part_a], points[part_b], (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame_zeros, points[part_a], points[part_b], colors[index], 3)
return frame_openposedef yolo(size, score_threshold, nms_threshold, custom=False):
# 네트워크 지정
if custom is True: # custom 모델
net = net_yolo_custom
classes = classes_custom
else: # coco 모델
net = net_yolo
classes = classes_coco
layer_names = net.getLayerNames()
output_layers = [layer_names[i[0] - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
# 이미지의 높이, 너비, 채널 받아오기
height, width, channels = frame.shape
# 네트워크에 넣기 위한 전처리
if custom is True: # custom 모델
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame_zeros, 0.00392, (size, size), (0, 0, 0), True, crop=False)
else: # coco 모델
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 0.00392, (size, size), (0, 0, 0), True, crop=False)
# 전처리된 blob 네트워크에 입력
net.setInput(blob)
# 결과 받아오기
outs = net.forward(output_layers)
# 각각의 데이터를 저장할 리스트 생성 및 초기화
class_ids = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
# custom 일 때는 coco 로 탐지했던 객체 정보들이 남아있어야 하므로
if custom is False:
nms_boxes.clear()
for out in outs:
for detection in out:
scores = detection[5:]
class_id = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[class_id]
if confidence > 0.1:
# 탐지된 객체의 너비, 높이 및 중앙 좌표값 찾기
center_x = int(detection[0] * width)
center_y = int(detection[1] * height)
w = int(detection[2] * width)
h = int(detection[3] * height)
# 객체의 사각형 테두리 중 좌상단 좌표값 찾기
x = int(center_x - w / 2)
y = int(center_y - h / 2)
boxes.append([x, y, w, h])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
class_ids.append(class_id)
# 노이즈 제거 (Non Maximum Suppression) (겹쳐있는 박스 중 상자가 물체일 확률이 가장 높은 박스만 남겨둠)
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, score_threshold=score_threshold, nms_threshold=nms_threshold)
for i in range(len(boxes)):
if i in indexes:
x, y, w, h = boxes[i]
class_name = classes[class_ids[i]]
if custom is False:
# 중복된 객체를 이름 뒤 숫자를 추가하여 구분
class_name += ' 1'
num = 1
while class_name in nms_boxes.keys():
num += 1
class_name = class_name[:-1] + str(num)
# 프레임에 작성할 텍스트 및 색깔 지정
label = f"{class_name}: {confidences[i]:.2f}"
if custom is True:
color = colors[class_ids[i] + len(classes_coco)]
else:
color = colors[class_ids[i]]
# 프레임에 사각형 테두리 그리기 및 텍스트 쓰기
cv2.rectangle(frame_yolo, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2)
cv2.rectangle(frame_yolo, (x - 1, y), (x + len(class_name) * 13 + 80, y - 25), color, -1)
cv2.putText(frame_yolo, label, (x, y - 8), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL, 1, (255, 255, 255), 2)
# 탐지된 객체의 정보 출력 및 nms_boxex 에 저장
nms_boxes[class_name] = [x, y, w, h]
if custom is True:
for key, value in in_box().items():
# 만약 LHip 이나 RHip 이 포함된 경우
if (11 in value) or (12 in value):
cv2.putText(frame_openpose, f"{class_name} on {key}", (0, height - 16), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL, 2, (0, 0, 255), 3)
return frame_yolo# 탐지된 각 객체의 테두리 안에 사람의 joint 포함 정보를 딕셔너리로 반환
def in_box():
dic = {}
for key, value in nms_boxes.items():
if key.split(' ')[0] != "person" and key.split(' ')[0] not in classes_custom: # person, classes_custom 객체 제외
points_list = []
for index, point in enumerate(points):
if point is not None: # point 가 없을 경우 제외
x = value[0]
y = value[1]
width = value[0] + value[2]
height = value[1] + value[3]
if (point[0] > x) and (point[0] < width) and (point[1] > y) and (point[1] < height):
points_list.append(index)
if len(points_list) > 0:
dic[key] = points_list
return dic# 실행하려는 ipynb 파일의 경로로 이동
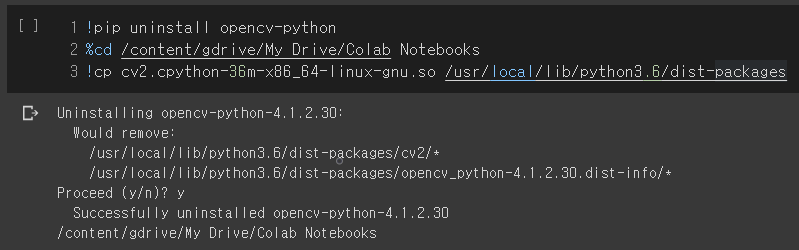
%cd /content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks
# 키포인트를 저장할 빈 리스트
points = []
# NMS 를 거친 객체 box 들의 정보를 저장할 딕셔너리 생성 (in_box() 함수에서 사용됨)
nms_boxes = {}
# 네트워크 불러오기
net_openpose = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoFile_body_25b, weightsFile_body_25b)
net_yolo = cv2.dnn.readNet("yolov4.weights", "yolov4.cfg")
net_yolo_custom = cv2.dnn.readNet("yolov4-custom.weights", "yolov4-custom.cfg")
# GPU 할당
net_openpose.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
net_openpose.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA)
net_yolo.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
net_yolo.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA)
net_yolo_custom.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
net_yolo_custom.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA)
# 입력 사이즈 리스트 (Yolo 에서 사용되는 네크워크 입력 이미지 사이즈)
size_list = [320, 416, 608]
# 클래스의 갯수만큼 랜덤 RGB 배열을 생성
colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(classes_coco) + len(classes_custom), 3))
# 비디오 경로
video = "../test_360_Trim.mp4"
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(video)
total_frame = int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
for now_frame in tqdm(range(total_frame)):
ret, frame = capture.read()
# 프레임 복사
frame_openpose = frame.copy()
frame_yolo = frame.copy()
# 이미지의 크기와 같은 검은색 프레임 생성
frame_zeros = np.zeros((frame.shape[0], frame.shape[1], 3), np.uint8)
# openpose (joint 포인팅)
output_keypoints(threshold=0.1, BODY_PARTS=BODY_PARTS_BODY_25B)
# 각 joint 를 선으로 연결한 프레임
output_keypoints_with_lines(POSE_PAIRS=POSE_PAIRS_BODY_25B)
# yolo (객체 탐지)
yolo(size_list[1], score_threshold=0.4, nms_threshold=0.4)
# yolo (자세 탐지)
yolo(size_list[1], score_threshold=0.4, nms_threshold=0.4, custom=True)
# 프레임 세로로 이어붙이기
frame_horizontal = cv2.vconcat([frame_openpose, frame_yolo])
# 이미지 파일 생성
cv2.imwrite(f"/content/gdrive/My Drive/frames_360/{now_frame:.0f}.jpg", frame_horizontal)
capture.release()구글 드라이브에 frames_360 폴더를 생성 후 위 코드까지 실행하면 해당 폴더 안에 영상의 각 프레임이 이미지 파일(jpg) 형태로 저장됨
import glob
img_array = []
for file in tqdm(glob.glob('/content/gdrive/My Drive/frames_360/*.jpg')):
img = cv2.imread(file)
img_array.append(img)
height, width = img.shape[:2]
size = (width, height)
video = cv2.VideoWriter('result.avi',cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'DIVX'), 20, size)
for img in img_array:
video.write(img)
video.release()위 코드를 통해 이미지 파일들을 비디오 형태로 변환 후 저장(result.avi)
cv2.VideoWriter(outputFile, fourcc, frame, size)
ㄴ outputFile (str) - 파일명
ㄴ fourcc - Codec 정보
ㄴ frame (float) - frame/초
ㄴ size (list) - 사이즈 ex: (640, 360)
yolov4-custom 학습에 쓰인 데이터셋
yolov4-custom.cfg
사용된 영상 - 320p (출처: youtu.be/7xj5TTDvHfY)
사용된 영상 - 720p (출처: youtu.be/7xj5TTDvHfY)
'코랩' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [코랩] 런타임 연결 유지 및 출력 삭제 (0) | 2021.06.07 |
|---|---|
| [코랩] CUDA - OpenCV 설치하기 (0) | 2020.08.20 |
| [코랩] Darknet 설치 및 커스텀 모델 학습하기 (1) | 2020.08.17 |


import cv2
import numpy as np
from google.colab.patches import cv2_imshow
from tqdm import tqdm
protoFile_body_25b = "pose_deploy.prototxt"
weightsFile_body_25b = "pose_iter_XXXXXX.caffemodel"
BODY_PARTS_BODY_25B = {0: "Nose", 1: "LEye", 2: "REye", 3: "LEar", 4: "REar", 5: "LShoulder", 6: "RSoulder",
7: "LElbow", 8: "RElbow", 9: "LWrist", 10: "RWrist", 11: "LHip", 12: "RHip", 13: "LKnee",
14: "RKnee", 15: "LAnkle", 16: "RAnkle", 17: "Neck", 18: "Head", 19: "LBigToe",
20: "LSmallToe", 21: "LHeel", 22: "RBigToe", 23: "RSmallToe", 24: "RHeel"}
POSE_PAIRS_BODY_25B = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 17], [0, 18], [1, 3], [2, 4], [5, 7], [5, 17],
[6, 8], [6, 17], [7, 9], [8, 10], [11, 13], [11, 17], [12, 14], [12, 17],
[13, 15], [14, 16], [15, 21], [16, 24], [19, 20], [20, 21], [22, 23], [23, 24]]
classes_coco = ["person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle",
"airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light", "fire hydrant",
"stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse",
"sheep", "cow", "elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack",
"umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee", "skis",
"snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard",
"surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife",
"spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog",
"pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch", "potted plant", "bed", "dining table",
"toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard",
"cell phone", "microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator",
"book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier", "toothbrush"]
classes_custom = ["sit", "stand", "lieDown"]
print(cv2.__version__)
print(cv2.cuda.getCudaEnabledDeviceCount())
def output_keypoints(threshold, BODY_PARTS):
global points
# 네트워크 지정
net = net_openpose
# 입력 이미지의 사이즈 정의
image_height = 368
image_width = 368
# 네트워크에 넣기 위한 전처리
input_blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1.0 / 255, (image_width, image_height), (0, 0, 0),
swapRB=False, crop=False)
# 전처리된 blob 네트워크에 입력
net.setInput(input_blob)
# 결과 받아오기
out = net.forward()
# The output is a 4D matrix :
# The first dimension being the image ID ( in case you pass more than one image to the network ).
# The second dimension indicates the index of a keypoint.
# The model produces Confidence Maps and Part Affinity maps which are all concatenated.
# For COCO model it consists of 57 parts – 18 keypoint confidence Maps + 1 background + 19*2 Part Affinity Maps. Similarly, for MPI, it produces 44 points.
# We will be using only the first few points which correspond to Keypoints.
# The third dimension is the height of the output map.
out_height = out.shape[2]
# The fourth dimension is the width of the output map.
out_width = out.shape[3]
# 원본 이미지의 높이, 너비를 받아오기
frame_height, frame_width = frame.shape[:2]
# 포인트 리스트 초기화
points = []
for i in range(len(BODY_PARTS)):
# 신체 부위의 confidence map
prob_map = out[0, i, :, :]
# 최소값, 최대값, 최소값 위치, 최대값 위치
min_val, prob, min_loc, point = cv2.minMaxLoc(prob_map)
# 원본 이미지에 맞게 포인트 위치 조정
x = (frame_width * point[0]) / out_width
x = int(x)
y = (frame_height * point[1]) / out_height
y = int(y)
if prob > threshold: # [pointed]
cv2.circle(frame_openpose, (x, y), 5, (0, 255, 255), thickness=-1, lineType=cv2.FILLED)
cv2.circle(frame_zeros, (x, y), 5, (0, 255, 255), thickness=-1, lineType=cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(frame_openpose, str(i), (x, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 1,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
points.append((x, y))
else: # [not pointed]
cv2.circle(frame_openpose, (x, y), 5, (0, 255, 255), thickness=-1, lineType=cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(frame_openpose, str(i), (x, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 0, 0), 1,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
points.append(None)
return frame_openposedef output_keypoints_with_lines(POSE_PAIRS):
# POSE_PAIRS 갯수만큼 RGB 배열을 생성 (frame_zeros에 쓰일 색)
colors = []
for i in range(3):
value_r = value_g = value_b = 50
for j in range(int(len(POSE_PAIRS_BODY_25B) / 3)):
if i == 0:
value_b += 31
if i == 1:
value_g += 31
if i == 2:
value_r += 31
colors.append((value_b, value_g, value_r))
for index, pair in enumerate(POSE_PAIRS):
part_a = pair[0] # 0 (Head)
part_b = pair[1] # 1 (Neck)
if points[part_a] and points[part_b]:
cv2.line(frame_openpose, points[part_a], points[part_b], (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame_zeros, points[part_a], points[part_b], colors[index], 3)
return frame_openposedef yolo(size, score_threshold, nms_threshold, custom=False):
# 네트워크 지정
if custom is True: # custom 모델
net = net_yolo_custom
classes = classes_custom
else: # coco 모델
net = net_yolo
classes = classes_coco
layer_names = net.getLayerNames()
output_layers = [layer_names[i[0] - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
# 이미지의 높이, 너비, 채널 받아오기
height, width, channels = frame.shape
# 네트워크에 넣기 위한 전처리
if custom is True: # custom 모델
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame_zeros, 0.00392, (size, size), (0, 0, 0), True, crop=False)
else: # coco 모델
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 0.00392, (size, size), (0, 0, 0), True, crop=False)
# 전처리된 blob 네트워크에 입력
net.setInput(blob)
# 결과 받아오기
outs = net.forward(output_layers)
# 각각의 데이터를 저장할 리스트 생성 및 초기화
class_ids = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
# custom 일 때는 coco 로 탐지했던 객체 정보들이 남아있어야 하므로
if custom is False:
nms_boxes.clear()
for out in outs:
for detection in out:
scores = detection[5:]
class_id = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[class_id]
if confidence > 0.1:
# 탐지된 객체의 너비, 높이 및 중앙 좌표값 찾기
center_x = int(detection[0] * width)
center_y = int(detection[1] * height)
w = int(detection[2] * width)
h = int(detection[3] * height)
# 객체의 사각형 테두리 중 좌상단 좌표값 찾기
x = int(center_x - w / 2)
y = int(center_y - h / 2)
boxes.append([x, y, w, h])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
class_ids.append(class_id)
# 노이즈 제거 (Non Maximum Suppression) (겹쳐있는 박스 중 상자가 물체일 확률이 가장 높은 박스만 남겨둠)
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, score_threshold=score_threshold, nms_threshold=nms_threshold)
for i in range(len(boxes)):
if i in indexes:
x, y, w, h = boxes[i]
class_name = classes[class_ids[i]]
if custom is False:
# 중복된 객체를 이름 뒤 숫자를 추가하여 구분
class_name += ' 1'
num = 1
while class_name in nms_boxes.keys():
num += 1
class_name = class_name[:-1] + str(num)
# 프레임에 작성할 텍스트 및 색깔 지정
label = f"{class_name}: {confidences[i]:.2f}"
if custom is True:
color = colors[class_ids[i] + len(classes_coco)]
else:
color = colors[class_ids[i]]
# 프레임에 사각형 테두리 그리기 및 텍스트 쓰기
cv2.rectangle(frame_yolo, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2)
cv2.rectangle(frame_yolo, (x - 1, y), (x + len(class_name) * 13 + 80, y - 25), color, -1)
cv2.putText(frame_yolo, label, (x, y - 8), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL, 1, (255, 255, 255), 2)
# 탐지된 객체의 정보 출력 및 nms_boxex 에 저장
nms_boxes[class_name] = [x, y, w, h]
if custom is True:
for key, value in in_box().items():
# 만약 LHip 이나 RHip 이 포함된 경우
if (11 in value) or (12 in value):
cv2.putText(frame_openpose, f"{class_name} on {key}", (0, height - 16), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL, 2, (0, 0, 255), 3)
return frame_yolo# 탐지된 각 객체의 테두리 안에 사람의 joint 포함 정보를 딕셔너리로 반환
def in_box():
dic = {}
for key, value in nms_boxes.items():
if key.split(' ')[0] != "person" and key.split(' ')[0] not in classes_custom: # person, classes_custom 객체 제외
points_list = []
for index, point in enumerate(points):
if point is not None: # point 가 없을 경우 제외
x = value[0]
y = value[1]
width = value[0] + value[2]
height = value[1] + value[3]
if (point[0] > x) and (point[0] < width) and (point[1] > y) and (point[1] < height):
points_list.append(index)
if len(points_list) > 0:
dic[key] = points_list
return dic# 실행하려는 ipynb 파일의 경로로 이동
%cd /content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks
# 키포인트를 저장할 빈 리스트
points = []
# NMS 를 거친 객체 box 들의 정보를 저장할 딕셔너리 생성 (in_box() 함수에서 사용됨)
nms_boxes = {}
# 네트워크 불러오기
net_openpose = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoFile_body_25b, weightsFile_body_25b)
net_yolo = cv2.dnn.readNet("yolov4.weights", "yolov4.cfg")
net_yolo_custom = cv2.dnn.readNet("yolov4-custom.weights", "yolov4-custom.cfg")
# GPU 할당
net_openpose.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
net_openpose.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA)
net_yolo.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
net_yolo.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA)
net_yolo_custom.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
net_yolo_custom.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA)
# 입력 사이즈 리스트 (Yolo 에서 사용되는 네크워크 입력 이미지 사이즈)
size_list = [320, 416, 608]
# 클래스의 갯수만큼 랜덤 RGB 배열을 생성
colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(classes_coco) + len(classes_custom), 3))
# 비디오 경로
video = "../test_360_Trim.mp4"
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(video)
total_frame = int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
for now_frame in tqdm(range(total_frame)):
ret, frame = capture.read()
# 프레임 복사
frame_openpose = frame.copy()
frame_yolo = frame.copy()
# 이미지의 크기와 같은 검은색 프레임 생성
frame_zeros = np.zeros((frame.shape[0], frame.shape[1], 3), np.uint8)
# openpose (joint 포인팅)
output_keypoints(threshold=0.1, BODY_PARTS=BODY_PARTS_BODY_25B)
# 각 joint 를 선으로 연결한 프레임
output_keypoints_with_lines(POSE_PAIRS=POSE_PAIRS_BODY_25B)
# yolo (객체 탐지)
yolo(size_list[1], score_threshold=0.4, nms_threshold=0.4)
# yolo (자세 탐지)
yolo(size_list[1], score_threshold=0.4, nms_threshold=0.4, custom=True)
# 프레임 세로로 이어붙이기
frame_horizontal = cv2.vconcat([frame_openpose, frame_yolo])
# 이미지 파일 생성
cv2.imwrite(f"/content/gdrive/My Drive/frames_360/{now_frame:.0f}.jpg", frame_horizontal)
capture.release()구글 드라이브에 frames_360 폴더를 생성 후 위 코드까지 실행하면 해당 폴더 안에 영상의 각 프레임이 이미지 파일(jpg) 형태로 저장됨
import glob
img_array = []
for file in tqdm(glob.glob('/content/gdrive/My Drive/frames_360/*.jpg')):
img = cv2.imread(file)
img_array.append(img)
height, width = img.shape[:2]
size = (width, height)
video = cv2.VideoWriter('result.avi',cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'DIVX'), 20, size)
for img in img_array:
video.write(img)
video.release()위 코드를 통해 이미지 파일들을 비디오 형태로 변환 후 저장(result.avi)
cv2.VideoWriter(outputFile, fourcc, frame, size)
ㄴ outputFile (str) - 파일명
ㄴ fourcc - Codec 정보
ㄴ frame (float) - frame/초
ㄴ size (list) - 사이즈 ex: (640, 360)
yolov4-custom 학습에 쓰인 데이터셋
yolov4-custom.cfg
사용된 영상 - 320p (출처: youtu.be/7xj5TTDvHfY)
사용된 영상 - 720p (출처: youtu.be/7xj5TTDvHfY)
'코랩' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [코랩] 런타임 연결 유지 및 출력 삭제 (0) | 2021.06.07 |
|---|---|
| [코랩] CUDA - OpenCV 설치하기 (0) | 2020.08.20 |
| [코랩] Darknet 설치 및 커스텀 모델 학습하기 (1) | 2020.08.17 |
